PPT The Arrhenius Equation PowerPoint Presentation, free download
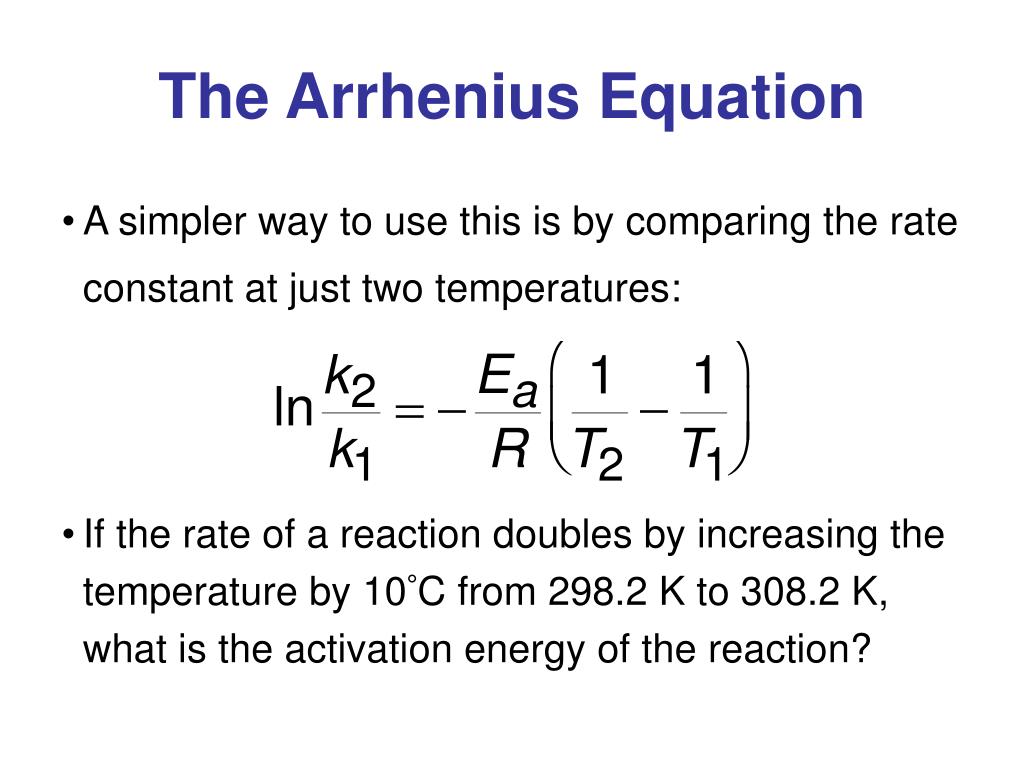
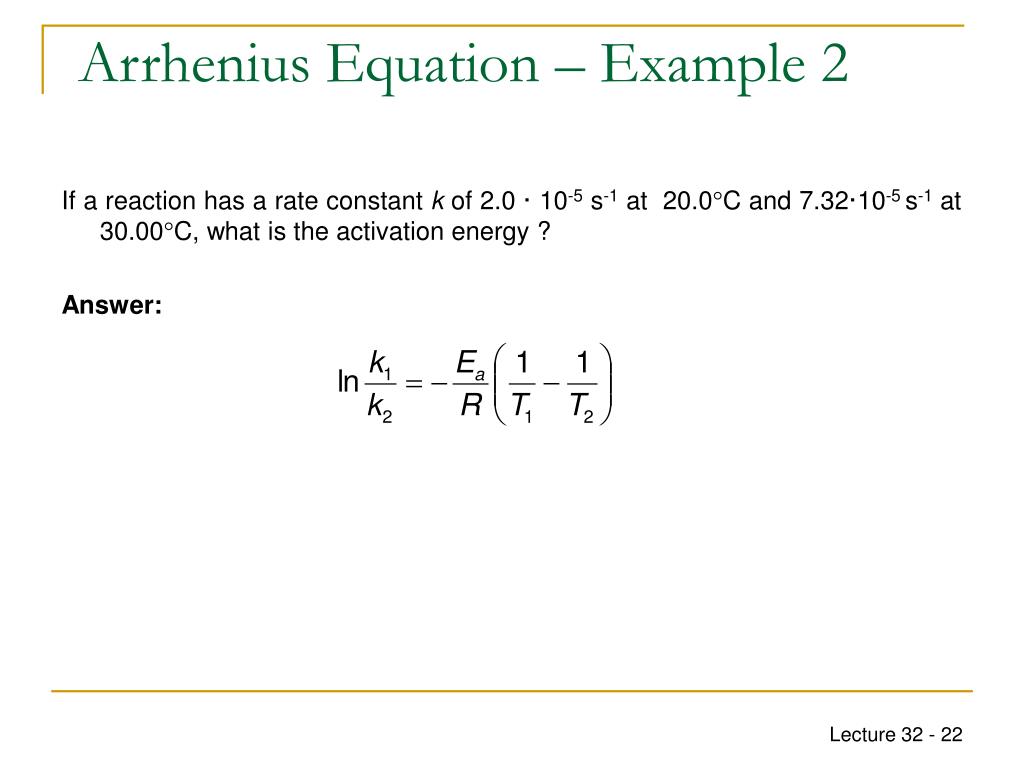
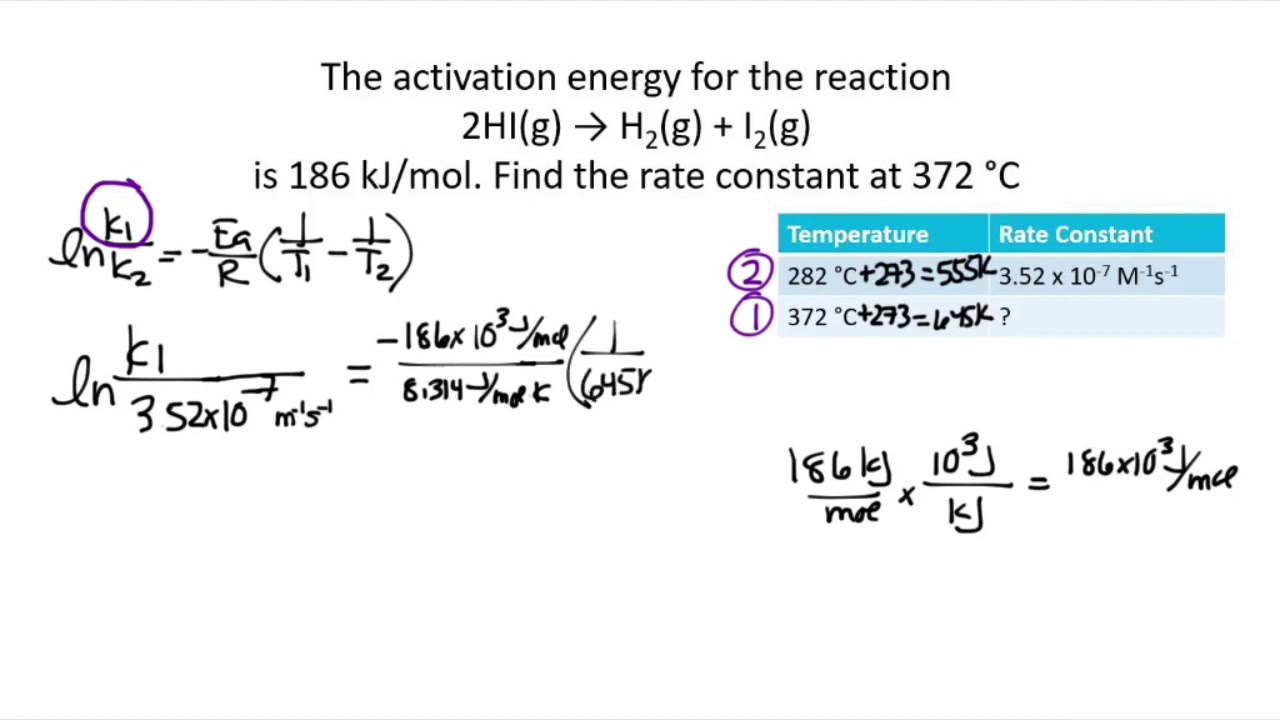
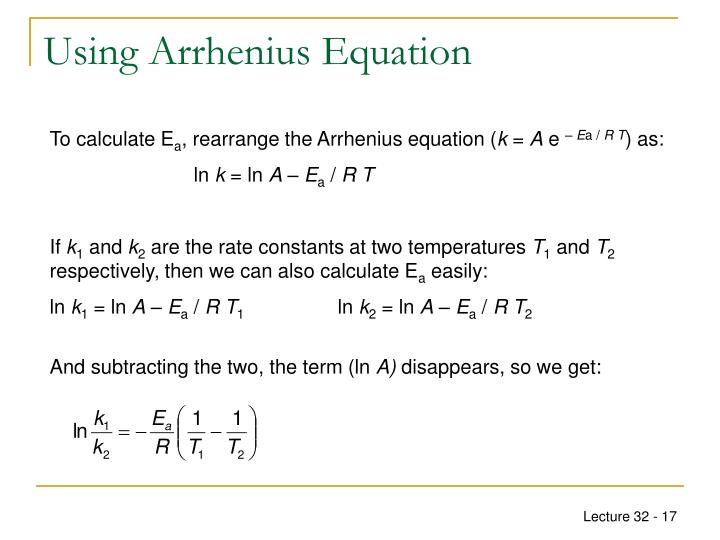
The Math / Science The Arrhenius Equation, k = A⋅ e− Ea RT k = A ⋅ e - E a RT, can be rewritten (as shown below) to show the change from k 1 to k 2 when a temperature change from T 1 to T 2 takes place. The Activation Energy equation using the Arrhenius formula is: Ea = R⋅ ln(k2 k1) 1 T 1 − 1 T 2 E a = R ⋅ ln ( k 2 k 1) 1 T 1 - 1 T 2 where:

Arrhenius Equation
The exponential term in the Arrhenius equation implies that the rate constant of a reaction increases exponentially when the activation energy decreases. Because the rate of a reaction is directly proportional to the rate constant of a reaction, the rate increases exponentially as well.. Calculate the activation energy if the pre-exponential.

Arrhenius Equation YouTube
The Arrhenius equation is a formula that describes how the rate of a reaction varied based on temperature, or the rate constant. If we look at the equation that this Arrhenius equation calculator uses, we can try to understand how it works: k = A\cdot \text {e}^ {-\frac {E_ {\text {a}}} {R\cdot T}}, k = A ⋅ e−R⋅T Ea, where:
Apply the Arrhenius equation to calculate how many ti… SolvedLib
Arrhenius equation calculator Natural Language Math Input Extended Keyboard Examples Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals. For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music…
PPT The Arrhenius Equation PowerPoint Presentation, free download
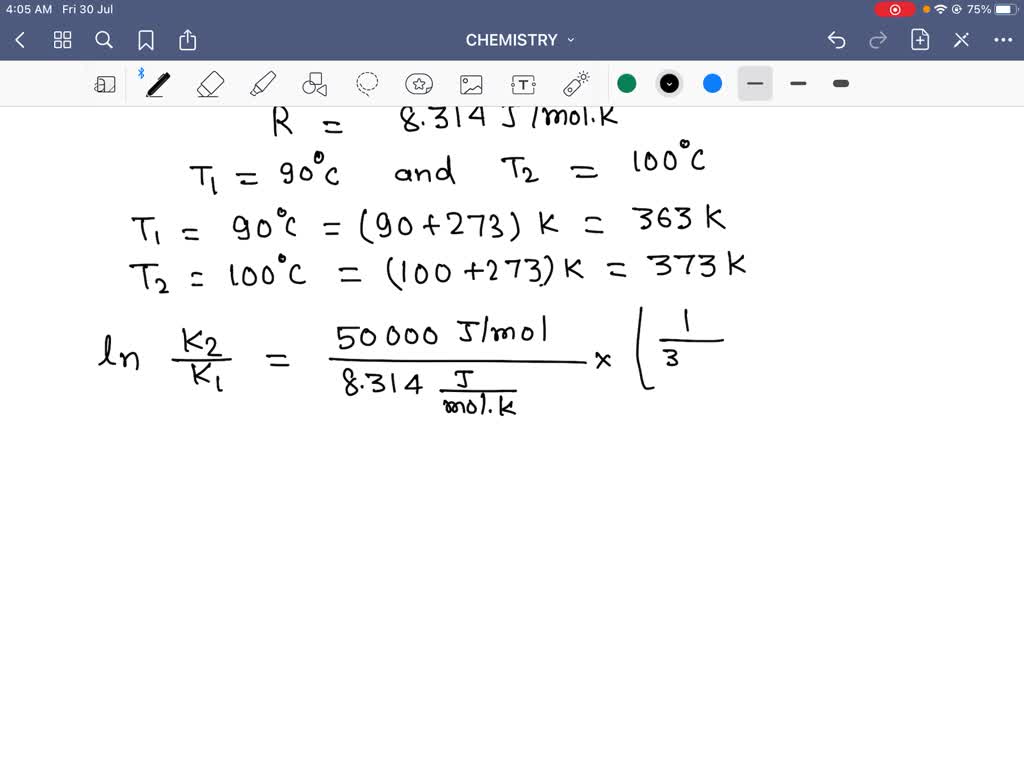
You can find the activation energy for any reactant using the Arrhenius equation: E_\mathrm {a} = -R × T × \ln\biggl (\frac {k} {A}\biggr) E a = −R × T × ln(Ak) where: R R — Gas constant. It is equal to \mathrm {8.314\ J/ (K\!\cdot\!mol)} 8.314 J/(K⋅mol); T T — Temperature of the surroundings, expressed in Kelvins; k k — Reaction rate coefficient.
30+ arrhenius equation calculator MujahidTaylore
Arrhenius Equation Calculator - Free Online Calculator Learn how to use the Arrhenius equation calculator with a step-by-step procedure. Get the Arrhenius equation calculator available online for free only at BYJU'S. Login Study Materials NCERT Solutions NCERT Solutions For Class 12 NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Physics
PPT The Arrhenius Equation PowerPoint Presentation, free download
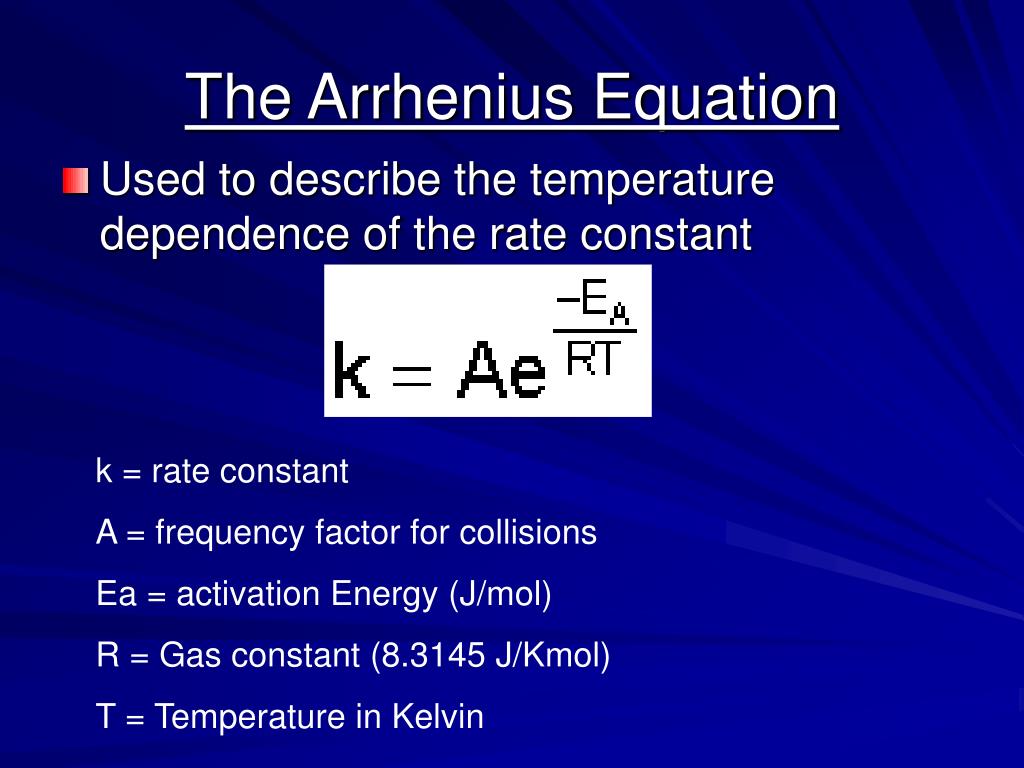
k = A × e - (Ea/RT) Where: k is the rate constant of the reaction, A is the pre-exponential factor, which is the rate constant at infinite temperature, E a is the activation energy of the reaction, R is the universal gas constant, and T is the absolute temperature in Kelvin. Real Life Application

Posada en caso Permanecer de pié arrhenius equation calculator al
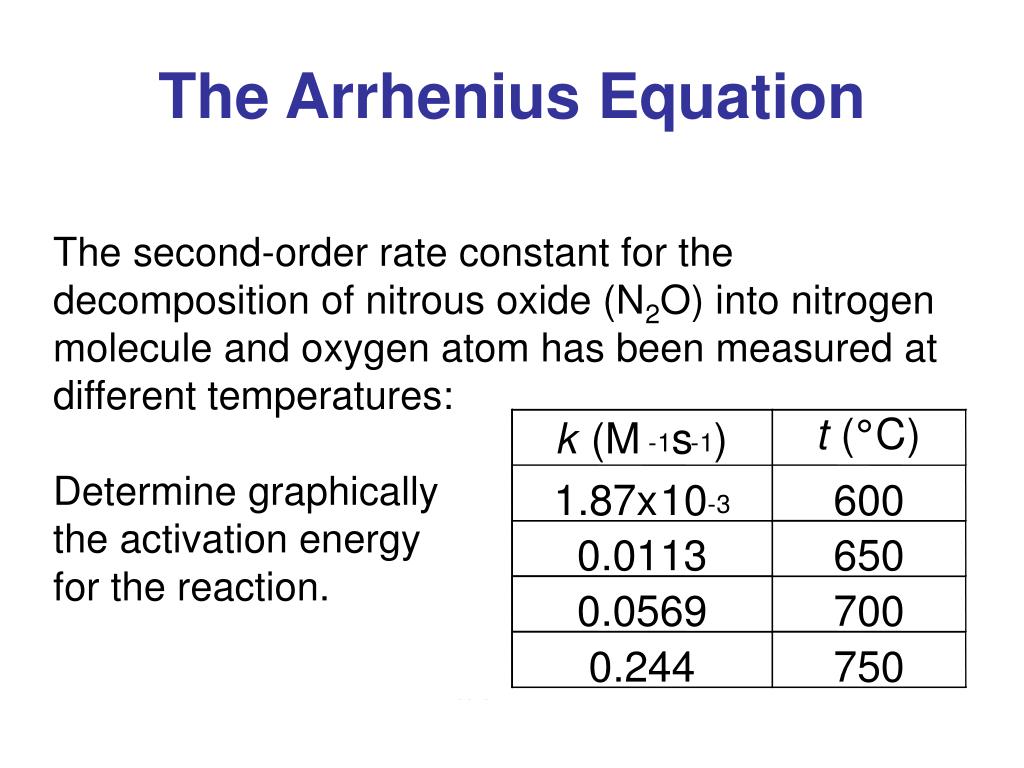
The Arrhenius equation is used to determine the activation energy or rate constant of a chemical reaction. as the temperature changes. If you want to see how the rate constant changes when the temperature changes, the Arrhenius equation is your friend.. Calculate the energy of activation for this chemical reaction. Solution: Since we are.
PPT CHEM1612 Pharmacy Week 11 Arrhenius Equation
The Arrhenius equation gives the dependence of the rate constant of a chemical reaction on the absolute temperature as where k is the rate constant (frequency of collisions resulting in a reaction), T is the absolute temperature (in Kelvin or degree Rankine ), A is the pre-exponential factor or Arrhenius factor or frequency factor.

16.2 The Arrhenius equation (HL) YouTube
The Arrhenius equation is used to calculate the rate constant (k) of a chemical reaction as a function of temperature (T), activation energy (Ea), and the pre-exponential factor (A). The equation is expressed as: k = A * exp (-Ea / (R * T)) Where: k is the rate constant A is the pre-exponential factor or frequency factor Ea is the activation energy
Worked Example with the Arrhenius Equation YouTube
This calculator calculates the effect of temperature on reaction rates using the Arrhenius equation. k=A*exp (-Ea/R*T) where k is the rate coefficient, A is a constant, E a is the activation energy, R is the universal gas constant, and T is the temperature (in degrees Kelvin). R has the value of 8.314 x 10 -3 kJ mol -1 K -1.

Arrhenius Calculations YouTube
The Arrhenius equation Forms of the Arrhenius equation Using the Arrhenius equation Collision theory and the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution Elementary reactions Reaction mechanism and rate law Reaction mechanism and rate law Multistep reaction energy profiles Catalysts Types of catalysts Types of catalysts Science > Chemistry library > Kinetics >

Arrhenius Equation Calculator Formula Example Calculator Academy
The Arrhenius equation, from a chemical point of view, is: k = A\cdot e^ {\frac {-E_ {\text {a}}} {R \cdot T}} k = A ⋅ e R⋅T −Ea We can identify many elements in the Arrhenius equation: k k is the rate constant, usually expressed in the units \text {M}^ {1-n}\text {s} M1−ns, where n n is the reaction order;
[Solved] Using Arrhenius equation to calculate the ratio 9to5Science
The Arrhenius equation is an expression that provides a relationship between the rate constant (of a chemical reaction), the absolute temperature, and the A factor (also known as the pre-exponential factor; can be visualized as the frequency of correctly oriented collisions between reactant particles).
PPT CHEM1612 Pharmacy Week 11 Arrhenius Equation
This calculator calculates the effect of temperature on reaction rates using the Arrhenius equation. k=A*exp (-Ea/R*T) where k is the rate coefficient, A is a constant, E is the activation energy, R is the universal gas constant, and T is the temperature (in kelvin). R has the value of 8.314 x 10 -3 kJ mol -1 K -1.

The Arrhenius Equation (A Level Chemistry) Teaching Resources
Arrhenius Equation Calculator. K = Rate Constant; A = Frequency Factor; EA = Activation Energy; T = Temperature; R = Universal Gas Constant ; Temperature has a profound influence on the rate of a reaction. Arrhenius showed that the rate constant (velocity constant) of a reaction increases exponentially with an increase in temperature.